Markov chain models
See also: Time series introduction, Time series modeling in finance, Autoregressive models, Credit ratings and Markov Chain models, Time series in ModelRisk
Markov Chains comprise a number of individuals who begin in certain allowed states of the system and who may or may not randomly change (transition) into other allowed states over time.
A Markov Chain has no memory, meaning that the joint distribution of how many individuals will be in each allowed state depends only on how many were in each state the moment before, not on the pathways that led there. This lack of memory is known as the Markov property. Markov chains come in two flavours: continuous time and discrete time. We will look at a discrete time process first because it is the easiest to model.
Discrete time Markov chain
In a discrete time Markov process the individuals can move between states only at set (usually equally spaced) intervals of time. Consider a set of 100 individuals in the following four marital states:
-
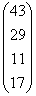
43 are Single
-
29 are Married
-
11 are Separated
-
17 are Divorced
We write this as a vector:
Given sufficient time (let's say a year) there is a reasonable probability that the individuals can change state. We can construct a matrix of the transition probabilities as follows:
|
Transition matrix |
Is now: |
||||
|
Single |
Married |
Separated |
Divorced |
||
|
Was: |
Single |
0.85 |
0.12 |
0.02 |
0.01 |
|
Married |
0 |
0.88 |
0.08 |
0.04 |
|
|
Separated |
0 |
0.13 |
0.45 |
0.42 |
|
|
Divorced |
0 |
0.09 |
0.02 |
0.89 |
|
We read this matrix row by row. For example, it says that (first row) a single person has an 85% chance of still being single one year later, a 12% chance of being married, a 2% chance of being separated and a 1% chance of being divorced. Since these are the only allowed states (e.g. we haven't included 'Engaged' so that must be rolled up into 'Single') the probabilities must sum to 100%. Of course we'd have to decide what a death would mean: the transition matrix could either be defined such that if a person dies they retain their marital status for this model, or we could make this a transition matrix conditional on them surviving a year.
Notice that the Single column is all 0's, except the Single/Single cell, because once one is married the only states allowed after that are Married, Separated and Divorced. Also not that one can go directly from Single to Separated or Divorced, which implies that during that year the individual had passed through the Married state. Markov chain transition matrices describe the probability that one is in a state at some precise time, given some state at a previous time, and is not concerned with how one got there, i.e. all the other states one might have passed through.
We now have the two elements of the model, the initial state vector and the transition matrix, to estimate how many individuals will be in each state after a year. Let's go through an example calculation to estimate how many people will be Married in one year:
-
For the Single people: Binomial(43,0.12) will be married
-
For the Married people: Binomial(29,0.88) will be married
-
For the Separated people: Binomial(11,0.13) will be married
-
For the Divorced people: Binomial(17,0.09) will be married
Add together these four Binomial distributions and we get an estimate of the number of people from our group who will be married next year. However, the above calculation does not work when we want to look at the joint distribution of how many people will be in each state: clearly we cannot add four sets of four Binomial distributions because the total must sum to 100 people. Instead, we need to use the Multinomial distribution. The number of people who were Single but are now {Single, Married, Separated, Divorced} equals Multinomial(43,{0.85, 0.12, 0.02, 0.01}). Applying the Multinomial distribution for the other three initial states we can take a random sample from each Multinomial and add up how many are in each state, as shown in the following model:
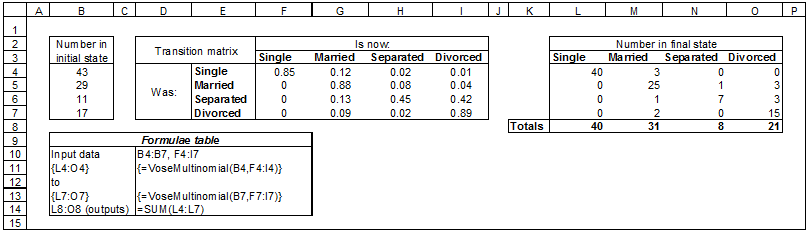
Example model ![]() Markov_chain_multinomial_method - Multinomial method of performing a Markov Chain model
Markov_chain_multinomial_method - Multinomial method of performing a Markov Chain model
Let's now look at extending the model to predict further ahead in time, say five years. If we can assume that the probability transition matrix remains valid for that period, and that nobody in our group dies, we could repeat the above exercise five times - calculating in each year how many individuals are in each state and using that as the input into the next year, etc. However, there is a more efficient method.
The probability a person starting in state i is in state j after two years is determined by looking at the probability of the person going from state i to each state after one year, and then going from that state to state j in the second year. So, for example, the probability of changing from Single to Divorced after two years is:
P(Single to Single) * P(Single to Divorced) +
P(Single to Married) * P(Married to Divorced) +
P(Single to Separated) * P(Separated to Divorced) +
P(Single to Divorced) * P(Divorced to Divorced)
=0.85*0.01 + 0.12*0.04 + 0.02*0.42 + 0.01*0.89 = 0.0306
Notice how we have multiplied the elements in the first row (Single) by the elements in the last column (Divorced) and added them. This is the operation performed in matrix multiplication. We can therefore determine the probability transition matrix over the two year period by simply multiplying the one year transition matrix by itself (using Excel's MMULT function) in the following model:
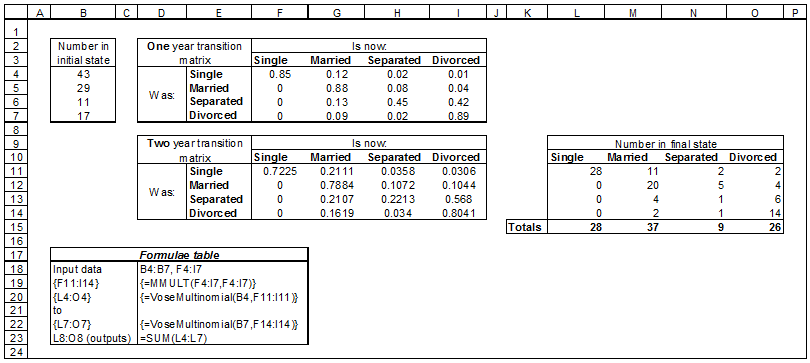
Example model ![]() Markov chain multinomial method 2 - multinomial method of performing a Markov Chain model with time an integer > 1 unit
Markov chain multinomial method 2 - multinomial method of performing a Markov Chain model with time an integer > 1 unit
When one wants to forecast T periods in advance where T is large, performing the matrix multiplication (T-1) times can become rather tedious, but there is some mathematics based on transforming the matrix that allows one to directly determine the transition matrix over any number of periods. ModelRisk provides some efficient means to do this: the VoseMarkovMatrix function calculates the transition matrix for any time length, and the VoseMarkovSample goes the next step, simulating how many individuals are in each final state after some period. In this next example we calculate the transition matrix and simulate how many individuals will be in each state after 25 years:
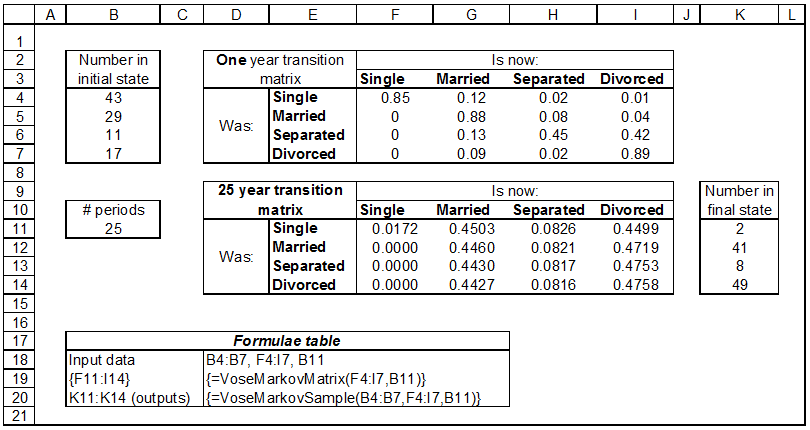
Example model ![]() Marital_status_in_25_years - ModelRisk methods for performing a Markov Chain model with time an integer > 1 unit
Marital_status_in_25_years - ModelRisk methods for performing a Markov Chain model with time an integer > 1 unit
Notice how after 25 years the probability of being Married is about 45% irrespective of what state one started in: a similar situation occurs for Separated and Divorced. This stabilizing property is very common and, as a matter of interest, is the basis of a statistical technique discussed briefly elsewhere in this help file. Of course, the above calculation does assume that the transition matrix for one year is valid to apply over such a long period (a big assumption in this case).
Application: credit ratings
Markov chain modeling is a useful tool for modeling the variation in a corporation's credit rating over time. This application is explained in the topic Credit ratings and Markov Chain models.
Continuous time Markov chain
For a continuous time Markov process we need to be able to produce the transition matrix for any positive time increment, not just an integer multiple of the time that applies to the base transition matrix. So, for example, we might have the above marital status transition matrix for a single year but wish to know what the matrix is for half a year, or 2.5 years.
There is a mathematical technique for finding the required matrix, based on converting the multinomial probabilities in the matrix into Poisson intensities that match the required probability. The mathematical manipulation is somewhat complex, particularly when one has to wrestle with numerical stability. The ModelRisk functions VoseMarkovMatrix and VoseMarkovSample detect when you are using non-integer time and automatically convert to the alternative mathematics.
Read on: Birth and death models
Navigation
- Risk management
- Risk management introduction
- What are risks and opportunities?
- Planning a risk analysis
- Clearly stating risk management questions
- Evaluating risk management options
- Introduction to risk analysis
- The quality of a risk analysis
- Using risk analysis to make better decisions
- Explaining a models assumptions
- Statistical descriptions of model outputs
- Simulation Statistical Results
- Preparing a risk analysis report
- Graphical descriptions of model outputs
- Presenting and using results introduction
- Statistical descriptions of model results
- Mean deviation (MD)
- Range
- Semi-variance and semi-standard deviation
- Kurtosis (K)
- Mean
- Skewness (S)
- Conditional mean
- Custom simulation statistics table
- Mode
- Cumulative percentiles
- Median
- Relative positioning of mode median and mean
- Variance
- Standard deviation
- Inter-percentile range
- Normalized measures of spread - the CofV
- Graphical descriptionss of model results
- Showing probability ranges
- Overlaying histogram plots
- Scatter plots
- Effect of varying number of bars
- Sturges rule
- Relationship between cdf and density (histogram) plots
- Difficulty of interpreting the vertical scale
- Stochastic dominance tests
- Risk-return plots
- Second order cumulative probability plot
- Ascending and descending cumulative plots
- Tornado plot
- Box Plot
- Cumulative distribution function (cdf)
- Probability density function (pdf)
- Crude sensitivity analysis for identifying important input distributions
- Pareto Plot
- Trend plot
- Probability mass function (pmf)
- Overlaying cdf plots
- Cumulative Plot
- Simulation data table
- Statistics table
- Histogram Plot
- Spider plot
- Determining the width of histogram bars
- Plotting a variable with discrete and continuous elements
- Smoothing a histogram plot
- Risk analysis modeling techniques
- Monte Carlo simulation
- Monte Carlo simulation introduction
- Monte Carlo simulation in ModelRisk
- Filtering simulation results
- Output/Input Window
- Simulation Progress control
- Running multiple simulations
- Random number generation in ModelRisk
- Random sampling from input distributions
- How many Monte Carlo samples are enough?
- Probability distributions
- Distributions introduction
- Probability calculations in ModelRisk
- Selecting the appropriate distributions for your model
- List of distributions by category
- Distribution functions and the U parameter
- Univariate continuous distributions
- Beta distribution
- Beta Subjective distribution
- Four-parameter Beta distribution
- Bradford distribution
- Burr distribution
- Cauchy distribution
- Chi distribution
- Chi Squared distribution
- Continuous distributions introduction
- Continuous fitted distribution
- Cumulative ascending distribution
- Cumulative descending distribution
- Dagum distribution
- Erlang distribution
- Error distribution
- Error function distribution
- Exponential distribution
- Exponential family of distributions
- Extreme Value Minimum distribution
- Extreme Value Maximum distribution
- F distribution
- Fatigue Life distribution
- Gamma distribution
- Generalized Extreme Value distribution
- Generalized Logistic distribution
- Generalized Trapezoid Uniform (GTU) distribution
- Histogram distribution
- Hyperbolic-Secant distribution
- Inverse Gaussian distribution
- Johnson Bounded distribution
- Johnson Unbounded distribution
- Kernel Continuous Unbounded distribution
- Kumaraswamy distribution
- Kumaraswamy Four-parameter distribution
- Laplace distribution
- Levy distribution
- Lifetime Two-Parameter distribution
- Lifetime Three-Parameter distribution
- Lifetime Exponential distribution
- LogGamma distribution
- Logistic distribution
- LogLaplace distribution
- LogLogistic distribution
- LogLogistic Alternative parameter distribution
- LogNormal distribution
- LogNormal Alternative-parameter distribution
- LogNormal base B distribution
- LogNormal base E distribution
- LogTriangle distribution
- LogUniform distribution
- Noncentral Chi squared distribution
- Noncentral F distribution
- Normal distribution
- Normal distribution with alternative parameters
- Maxwell distribution
- Normal Mix distribution
- Relative distribution
- Ogive distribution
- Pareto (first kind) distribution
- Pareto (second kind) distribution
- Pearson Type 5 distribution
- Pearson Type 6 distribution
- Modified PERT distribution
- PERT distribution
- PERT Alternative-parameter distribution
- Reciprocal distribution
- Rayleigh distribution
- Skew Normal distribution
- Slash distribution
- SplitTriangle distribution
- Student-t distribution
- Three-parameter Student distribution
- Triangle distribution
- Triangle Alternative-parameter distribution
- Uniform distribution
- Weibull distribution
- Weibull Alternative-parameter distribution
- Three-Parameter Weibull distribution
- Univariate discrete distributions
- Discrete distributions introduction
- Bernoulli distribution
- Beta-Binomial distribution
- Beta-Geometric distribution
- Beta-Negative Binomial distribution
- Binomial distribution
- Burnt Finger Poisson distribution
- Delaporte distribution
- Discrete distribution
- Discrete Fitted distribution
- Discrete Uniform distribution
- Geometric distribution
- HypergeoM distribution
- Hypergeometric distribution
- HypergeoD distribution
- Inverse Hypergeometric distribution
- Logarithmic distribution
- Negative Binomial distribution
- Poisson distribution
- Poisson Uniform distribution
- Polya distribution
- Skellam distribution
- Step Uniform distribution
- Zero-modified counting distributions
- More on probability distributions
- Multivariate distributions
- Multivariate distributions introduction
- Dirichlet distribution
- Multinomial distribution
- Multivariate Hypergeometric distribution
- Multivariate Inverse Hypergeometric distribution type2
- Negative Multinomial distribution type 1
- Negative Multinomial distribution type 2
- Multivariate Inverse Hypergeometric distribution type1
- Multivariate Normal distribution
- More on probability distributions
- Approximating one distribution with another
- Approximations to the Inverse Hypergeometric Distribution
- Normal approximation to the Gamma Distribution
- Normal approximation to the Poisson Distribution
- Approximations to the Hypergeometric Distribution
- Stirlings formula for factorials
- Normal approximation to the Beta Distribution
- Approximation of one distribution with another
- Approximations to the Negative Binomial Distribution
- Normal approximation to the Student-t Distribution
- Approximations to the Binomial Distribution
- Normal_approximation_to_the_Binomial_distribution
- Poisson_approximation_to_the_Binomial_distribution
- Normal approximation to the Chi Squared Distribution
- Recursive formulas for discrete distributions
- Normal approximation to the Lognormal Distribution
- Normal approximations to other distributions
- Approximating one distribution with another
- Correlation modeling in risk analysis
- Common mistakes when adapting spreadsheet models for risk analysis
- More advanced risk analysis methods
- SIDs
- Modeling with objects
- ModelRisk database connectivity functions
- PK/PD modeling
- Value of information techniques
- Simulating with ordinary differential equations (ODEs)
- Optimization of stochastic models
- ModelRisk optimization extension introduction
- Optimization Settings
- Defining Simulation Requirements in an Optimization Model
- Defining Decision Constraints in an Optimization Model
- Optimization Progress control
- Defining Targets in an Optimization Model
- Defining Decision Variables in an Optimization Model
- Optimization Results
- Summing random variables
- Aggregate distributions introduction
- Aggregate modeling - Panjer's recursive method
- Adding correlation in aggregate calculations
- Sum of a random number of random variables
- Moments of an aggregate distribution
- Aggregate modeling in ModelRisk
- Aggregate modeling - Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) method
- How many random variables add up to a fixed total
- Aggregate modeling - compound Poisson approximation
- Aggregate modeling - De Pril's recursive method
- Testing and modeling causal relationships
- Stochastic time series
- Time series introduction
- Time series in ModelRisk
- Autoregressive models
- Thiel inequality coefficient
- Effect of an intervention at some uncertain point in time
- Log return of a Time Series
- Markov Chain models
- Seasonal time series
- Bounded random walk
- Time series modeling in finance
- Birth and death models
- Time series models with leading indicators
- Geometric Brownian Motion models
- Time series projection of events occurring randomly in time
- Simulation for six sigma
- ModelRisk's Six Sigma functions
- VoseSixSigmaCp
- VoseSixSigmaCpkLower
- VoseSixSigmaProbDefectShift
- VoseSixSigmaLowerBound
- VoseSixSigmaK
- VoseSixSigmaDefectShiftPPMUpper
- VoseSixSigmaDefectShiftPPMLower
- VoseSixSigmaDefectShiftPPM
- VoseSixSigmaCpm
- VoseSixSigmaSigmaLevel
- VoseSixSigmaCpkUpper
- VoseSixSigmaCpk
- VoseSixSigmaDefectPPM
- VoseSixSigmaProbDefectShiftLower
- VoseSixSigmaProbDefectShiftUpper
- VoseSixSigmaYield
- VoseSixSigmaUpperBound
- VoseSixSigmaZupper
- VoseSixSigmaZmin
- VoseSixSigmaZlower
- Modeling expert opinion
- Modeling expert opinion introduction
- Sources of error in subjective estimation
- Disaggregation
- Distributions used in modeling expert opinion
- A subjective estimate of a discrete quantity
- Incorporating differences in expert opinions
- Modeling opinion of a variable that covers several orders of magnitude
- Maximum entropy
- Probability theory and statistics
- Probability theory and statistics introduction
- Stochastic processes
- Stochastic processes introduction
- Poisson process
- Hypergeometric process
- The hypergeometric process
- Number in a sample with a particular characteristic in a hypergeometric process
- Number of hypergeometric samples to get a specific number of successes
- Number of samples taken to have an observed s in a hypergeometric process
- Estimate of population and sub-population sizes in a hypergeometric process
- The binomial process
- Renewal processes
- Mixture processes
- Martingales
- Estimating model parameters from data
- The basics
- Probability equations
- Probability theorems and useful concepts
- Probability parameters
- Probability rules and diagrams
- The definition of probability
- The basics of probability theory introduction
- Fitting probability models to data
- Fitting time series models to data
- Fitting correlation structures to data
- Fitting in ModelRisk
- Fitting probability distributions to data
- Fitting distributions to data
- Method of Moments (MoM)
- Check the quality of your data
- Kolmogorov-Smirnoff (K-S) Statistic
- Anderson-Darling (A-D) Statistic
- Goodness of fit statistics
- The Chi-Squared Goodness-of-Fit Statistic
- Determining the joint uncertainty distribution for parameters of a distribution
- Using Method of Moments with the Bootstrap
- Maximum Likelihood Estimates (MLEs)
- Fitting a distribution to truncated censored or binned data
- Critical Values and Confidence Intervals for Goodness-of-Fit Statistics
- Matching the properties of the variable and distribution
- Transforming discrete data before performing a parametric distribution fit
- Does a parametric distribution exist that is well known to fit this type of variable?
- Censored data
- Fitting a continuous non-parametric second-order distribution to data
- Goodness of Fit Plots
- Fitting a second order Normal distribution to data
- Using Goodness-of Fit Statistics to optimize Distribution Fitting
- Information criteria - SIC HQIC and AIC
- Fitting a second order parametric distribution to observed data
- Fitting a distribution for a continuous variable
- Does the random variable follow a stochastic process with a well-known model?
- Fitting a distribution for a discrete variable
- Fitting a discrete non-parametric second-order distribution to data
- Fitting a continuous non-parametric first-order distribution to data
- Fitting a first order parametric distribution to observed data
- Fitting a discrete non-parametric first-order distribution to data
- Fitting distributions to data
- Technical subjects
- Comparison of Classical and Bayesian methods
- Comparison of classic and Bayesian estimate of Normal distribution parameters
- Comparison of classic and Bayesian estimate of intensity lambda in a Poisson process
- Comparison of classic and Bayesian estimate of probability p in a binomial process
- Which technique should you use?
- Comparison of classic and Bayesian estimate of mean "time" beta in a Poisson process
- Classical statistics
- Bayesian
- Bootstrap
- The Bootstrap
- Linear regression parametric Bootstrap
- The Jackknife
- Multiple variables Bootstrap Example 2: Difference between two population means
- Linear regression non-parametric Bootstrap
- The parametric Bootstrap
- Bootstrap estimate of prevalence
- Estimating parameters for multiple variables
- Example: Parametric Bootstrap estimate of the mean of a Normal distribution with known standard deviation
- The non-parametric Bootstrap
- Example: Parametric Bootstrap estimate of mean number of calls per hour at a telephone exchange
- The Bootstrap likelihood function for Bayesian inference
- Multiple variables Bootstrap Example 1: Estimate of regression parameters
- Bayesian inference
- Uninformed priors
- Conjugate priors
- Prior distributions
- Bayesian analysis with threshold data
- Bayesian analysis example: gender of a random sample of people
- Informed prior
- Simulating a Bayesian inference calculation
- Hyperparameters
- Hyperparameter example: Micro-fractures on turbine blades
- Constructing a Bayesian inference posterior distribution in Excel
- Bayesian analysis example: Tigers in the jungle
- Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) simulation
- Introduction to Bayesian inference concepts
- Bayesian estimate of the mean of a Normal distribution with known standard deviation
- Bayesian estimate of the mean of a Normal distribution with unknown standard deviation
- Determining prior distributions for correlated parameters
- Improper priors
- The Jacobian transformation
- Subjective prior based on data
- Taylor series approximation to a Bayesian posterior distribution
- Bayesian analysis example: The Monty Hall problem
- Determining prior distributions for uncorrelated parameters
- Subjective priors
- Normal approximation to the Beta posterior distribution
- Bayesian analysis example: identifying a weighted coin
- Bayesian estimate of the standard deviation of a Normal distribution with known mean
- Likelihood functions
- Bayesian estimate of the standard deviation of a Normal distribution with unknown mean
- Determining a prior distribution for a single parameter estimate
- Simulating from a constructed posterior distribution
- Bootstrap
- Comparison of Classical and Bayesian methods
- Analyzing and using data introduction
- Data Object
- Vose probability calculation
- Bayesian model averaging
- Miscellaneous
- Excel and ModelRisk model design and validation techniques
- Using range names for model clarity
- Color coding models for clarity
- Compare with known answers
- Checking units propagate correctly
- Stressing parameter values
- Model Validation and behavior introduction
- Informal auditing
- Analyzing outputs
- View random scenarios on screen and check for credibility
- Split up complex formulas (megaformulas)
- Building models that are efficient
- Comparing predictions against reality
- Numerical integration
- Comparing results of alternative models
- Building models that are easy to check and modify
- Model errors
- Model design introduction
- About array functions in Excel
- Excel and ModelRisk model design and validation techniques
- Monte Carlo simulation
- RISK ANALYSIS SOFTWARE
- Risk analysis software from Vose Software
- ModelRisk - risk modeling in Excel
- ModelRisk functions explained
- VoseCopulaOptimalFit and related functions
- VoseTimeOptimalFit and related functions
- VoseOptimalFit and related functions
- VoseXBounds
- VoseCLTSum
- VoseAggregateMoments
- VoseRawMoments
- VoseSkewness
- VoseMoments
- VoseKurtosis
- VoseAggregatePanjer
- VoseAggregateFFT
- VoseCombined
- VoseCopulaBiGumbel
- VoseCopulaBiClayton
- VoseCopulaBiNormal
- VoseCopulaBiT
- VoseKendallsTau
- VoseRiskEvent
- VoseCopulaBiFrank
- VoseCorrMatrix
- VoseRank
- VoseValidCorrmat
- VoseSpearman
- VoseCopulaData
- VoseCorrMatrixU
- VoseTimeSeasonalGBM
- VoseMarkovSample
- VoseMarkovMatrix
- VoseThielU
- VoseTimeEGARCH
- VoseTimeAPARCH
- VoseTimeARMA
- VoseTimeDeath
- VoseTimeAR1
- VoseTimeAR2
- VoseTimeARCH
- VoseTimeMA2
- VoseTimeGARCH
- VoseTimeGBMJDMR
- VoseTimePriceInflation
- VoseTimeGBMMR
- VoseTimeWageInflation
- VoseTimeLongTermInterestRate
- VoseTimeMA1
- VoseTimeGBM
- VoseTimeGBMJD
- VoseTimeShareYields
- VoseTimeYule
- VoseTimeShortTermInterestRate
- VoseDominance
- VoseLargest
- VoseSmallest
- VoseShift
- VoseStopSum
- VoseEigenValues
- VosePrincipleEsscher
- VoseAggregateMultiFFT
- VosePrincipleEV
- VoseCopulaMultiNormal
- VoseRunoff
- VosePrincipleRA
- VoseSumProduct
- VosePrincipleStdev
- VosePoissonLambda
- VoseBinomialP
- VosePBounds
- VoseAIC
- VoseHQIC
- VoseSIC
- VoseOgive1
- VoseFrequency
- VoseOgive2
- VoseNBootStdev
- VoseNBoot
- VoseSimulate
- VoseNBootPaired
- VoseAggregateMC
- VoseMean
- VoseStDev
- VoseAggregateMultiMoments
- VoseDeduct
- VoseExpression
- VoseLargestSet
- VoseKthSmallest
- VoseSmallestSet
- VoseKthLargest
- VoseNBootCofV
- VoseNBootPercentile
- VoseExtremeRange
- VoseNBootKurt
- VoseCopulaMultiClayton
- VoseNBootMean
- VoseTangentPortfolio
- VoseNBootVariance
- VoseNBootSkewness
- VoseIntegrate
- VoseInterpolate
- VoseCopulaMultiGumbel
- VoseCopulaMultiT
- VoseAggregateMultiMC
- VoseCopulaMultiFrank
- VoseTimeMultiMA1
- VoseTimeMultiMA2
- VoseTimeMultiGBM
- VoseTimeMultBEKK
- VoseAggregateDePril
- VoseTimeMultiAR1
- VoseTimeWilkie
- VoseTimeDividends
- VoseTimeMultiAR2
- VoseRuinFlag
- VoseRuinTime
- VoseDepletionShortfall
- VoseDepletion
- VoseDepletionFlag
- VoseDepletionTime
- VosejProduct
- VoseCholesky
- VoseTimeSimulate
- VoseNBootSeries
- VosejkProduct
- VoseRuinSeverity
- VoseRuin
- VosejkSum
- VoseTimeDividendsA
- VoseRuinNPV
- VoseTruncData
- VoseSample
- VoseIdentity
- VoseCopulaSimulate
- VoseSortA
- VoseFrequencyCumulA
- VoseAggregateDeduct
- VoseMeanExcessP
- VoseProb10
- VoseSpearmanU
- VoseSortD
- VoseFrequencyCumulD
- VoseRuinMaxSeverity
- VoseMeanExcessX
- VoseRawMoment3
- VosejSum
- VoseRawMoment4
- VoseNBootMoments
- VoseVariance
- VoseTimeShortTermInterestRateA
- VoseTimeLongTermInterestRateA
- VoseProb
- VoseDescription
- VoseCofV
- VoseAggregateProduct
- VoseEigenVectors
- VoseTimeWageInflationA
- VoseRawMoment1
- VosejSumInf
- VoseRawMoment2
- VoseShuffle
- VoseRollingStats
- VoseSplice
- VoseTSEmpiricalFit
- VoseTimeShareYieldsA
- VoseParameters
- VoseAggregateTranche
- VoseCovToCorr
- VoseCorrToCov
- VoseLLH
- VoseTimeSMEThreePoint
- VoseDataObject
- VoseCopulaDataSeries
- VoseDataRow
- VoseDataMin
- VoseDataMax
- VoseTimeSME2Perc
- VoseTimeSMEUniform
- VoseTimeSMESaturation
- VoseOutput
- VoseInput
- VoseTimeSMEPoisson
- VoseTimeBMAObject
- VoseBMAObject
- VoseBMAProb10
- VoseBMAProb
- VoseCopulaBMA
- VoseCopulaBMAObject
- VoseTimeEmpiricalFit
- VoseTimeBMA
- VoseBMA
- VoseSimKurtosis
- VoseOptConstraintMin
- VoseSimProbability
- VoseCurrentSample
- VoseCurrentSim
- VoseLibAssumption
- VoseLibReference
- VoseSimMoments
- VoseOptConstraintMax
- VoseSimMean
- VoseOptDecisionContinuous
- VoseOptRequirementEquals
- VoseOptRequirementMax
- VoseOptRequirementMin
- VoseOptTargetMinimize
- VoseOptConstraintEquals
- VoseSimVariance
- VoseSimSkewness
- VoseSimTable
- VoseSimCofV
- VoseSimPercentile
- VoseSimStDev
- VoseOptTargetValue
- VoseOptTargetMaximize
- VoseOptDecisionDiscrete
- VoseSimMSE
- VoseMin
- VoseMin
- VoseOptDecisionList
- VoseOptDecisionBoolean
- VoseOptRequirementBetween
- VoseOptConstraintBetween
- VoseSimMax
- VoseSimSemiVariance
- VoseSimSemiStdev
- VoseSimMeanDeviation
- VoseSimMin
- VoseSimCVARp
- VoseSimCVARx
- VoseSimCorrelation
- VoseSimCorrelationMatrix
- VoseOptConstraintString
- VoseOptCVARx
- VoseOptCVARp
- VoseOptPercentile
- VoseSimValue
- VoseSimStop
- Precision Control Functions
- VoseAggregateDiscrete
- VoseTimeMultiGARCH
- VoseTimeGBMVR
- VoseTimeGBMAJ
- VoseTimeGBMAJVR
- VoseSID
- Generalized Pareto Distribution (GPD)
- Generalized Pareto Distribution (GPD) Equations
- Three-Point Estimate Distribution
- Three-Point Estimate Distribution Equations
- VoseCalibrate
- ModelRisk interfaces
- Integrate
- Data Viewer
- Stochastic Dominance
- Library
- Correlation Matrix
- Portfolio Optimization Model
- Common elements of ModelRisk interfaces
- Risk Event
- Extreme Values
- Select Distribution
- Combined Distribution
- Aggregate Panjer
- Interpolate
- View Function
- Find Function
- Deduct
- Ogive
- AtRISK model converter
- Aggregate Multi FFT
- Stop Sum
- Crystal Ball model converter
- Aggregate Monte Carlo
- Splicing Distributions
- Subject Matter Expert (SME) Time Series Forecasts
- Aggregate Multivariate Monte Carlo
- Ordinary Differential Equation tool
- Aggregate FFT
- More on Conversion
- Multivariate Copula
- Bivariate Copula
- Univariate Time Series
- Modeling expert opinion in ModelRisk
- Multivariate Time Series
- Sum Product
- Aggregate DePril
- Aggregate Discrete
- Expert
- ModelRisk introduction
- Building and running a simple example model
- Distributions in ModelRisk
- List of all ModelRisk functions
- Custom applications and macros
- ModelRisk functions explained
- Tamara - project risk analysis
- Introduction to Tamara project risk analysis software
- Launching Tamara
- Importing a schedule
- Assigning uncertainty to the amount of work in the project
- Assigning uncertainty to productivity levels in the project
- Adding risk events to the project schedule
- Adding cost uncertainty to the project schedule
- Saving the Tamara model
- Running a Monte Carlo simulation in Tamara
- Reviewing the simulation results in Tamara
- Using Tamara results for cost and financial risk analysis
- Creating, updating and distributing a Tamara report
- Tips for creating a schedule model suitable for Monte Carlo simulation
- Random number generator and sampling algorithms used in Tamara
- Probability distributions used in Tamara
- Correlation with project schedule risk analysis
- Pelican - enterprise risk management